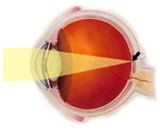
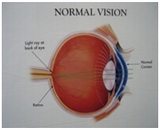
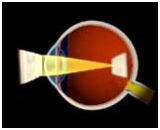
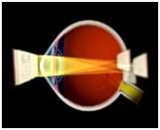
In a normal eye when rays of light pass through the lens and
cornea at the front of the eye, they are bent or refracted
and come to a focal point on the macula, a part of the
retina at the back of the eye.
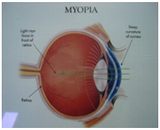
MYOPIA ( NEARSIGHTEDNESS )
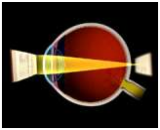
When the light rays focus on a focal point in front of the
retina as the eyeball may be too long or the lens system
has too much focusing power, this refractive error is
called myopia or nearsightedness. In people with myopia
distant objects are blurry, close objects are clear.
HYPEROPIA ( FARSIGHTEDNESS )
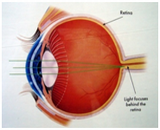
When the light rays focus on a focal point behind the retina
as the eyeball is too short or the focusing power of the lens
is too weak, this error is called hyperopia or farsightedness.
In people with hyperopia, distant objects and up close objects
are blurry.
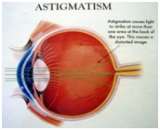
ASTIGMATISM
When the light rays cannot focus on a single focal point,
but focuses on more than one point on the retina as there
is distortion in the shape of the cornea, this refractive
error is called astigmatism. Astigmatism is often
responsible for starbursts, "ghosting" images, and halos
or rings around lights at night. Astigmatism can be
corrected with glasses or GP contact lenses.
All these refractive errors can be corrected surgically with LASIK
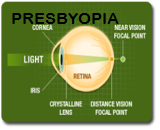
PRESBYOPIA
Decrease in flexibility of natural lens due to aging doesn’t
allow to focus on close vision and this compromises the
eye's ability to accommodate or switch from one focal point
(objects at a distance – driving) to another focal point
(objects that are close – reading). There may be eye fatigue
along with headaches when doing close work. This occurs
around the age of 40 and is known as presbyopia. No exercise
or medications can reverse presbyopia. Conductive
keratoplasty is a new procedure where the cornea is
flattened temporarily, but has to be repeated as the power
of refraction needed for near usually increases as one grows
older.